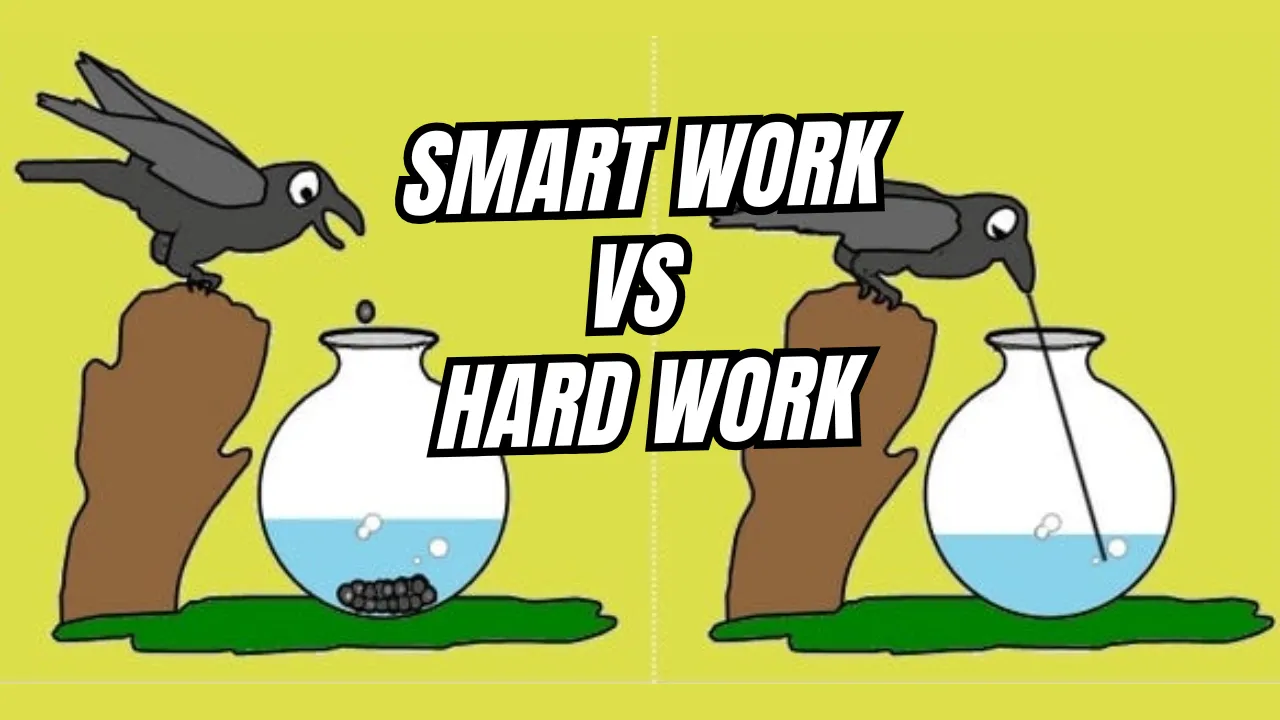
When it comes to achieving success, we often hear two common pieces of advice—“Work hard” and “Work smart.”ut which one is more effective? Are they mutually exclusive, or can they complement each other? The debate of Smart Work vs Hard Work has existed for ages, leaving many wondering which approach will lead to better results. While hard work emphasizes persistence, effort, and dedication, smart work focuses on efficiency, planning, and strategy. In today’s fast-paced world, where time is of the essence, understanding the difference and finding the right balance between the two is crucial for achieving your goals.
Smart Work vs Hard Work
To better grasp the concept of Smart Work vs Hard Work, think of a simple example: In ancient times, humans manually pushed heavy stones or carts to move goods. Over time, someone invented the wheelbarrow—a tool that allowed the same task to be done with far less effort and more efficiency. The early method represents hard work, while the invention of the wheelbarrow is a classic case of smart work.
Both hard work and smart work are essential, but knowing when and how to apply each is what makes the difference. While hard work builds character, discipline, and endurance, smart work ensures that the same tasks are accomplished in a more time-efficient and strategic manner.
Overview Table: Smart Work vs Hard Work at a Glance
| Feature | Hard Work | Smart Work |
| Approach | Focuses on effort, persistence, and time investment | Focuses on planning, strategy, and efficiency |
| Method | Traditional methods, consistent efforts | Innovative techniques, optimized processes |
| Time Consumption | Time-consuming | Saves time |
| Requirements | Dedication, patience, and physical effort | In-depth knowledge, logical thinking, and organization |
| Results | May take longer to achieve results | Often leads to faster achievement of goals |
| Key Benefit | Builds discipline, long-term persistence | Encourages creativity, time management, and effective solutions |
| Best Approach | Suitable for tasks needing repeated effort | Best for complex tasks needing smart solutions |
| Ideal Combination | Combining both ensures sustainable success | Combining both ensures sustainable success |
Hard Work: Stepping Stones of Success
Hard work is the foundation of growth, discipline, and success. It requires unwavering commitment, sincerity, and a willingness to put in consistent effort, even when the process seems tedious or slow.
Key Characteristics of Hard Work:
- Commitment: A hard-working person is dedicated to their goal, continuously working towards it regardless of the challenges faced.
- Traditional Approach: It sticks to conventional ways without necessarily seeking shortcuts or innovations.
- Time-Intensive: Hard work demands long hours and significant energy, often at the cost of personal comfort and leisure.
- Consistency: Perseverance plays a crucial role, especially when tasks are repetitive or difficult.
However, hard work alone may not always guarantee immediate results, and relying solely on it might cause exhaustion without maximizing efficiency.
Smart Work: The Efficient Way Forward
Smart work focuses on achieving maximum output with minimum effort. It involves analyzing the task, organizing resources, and using innovative strategies to complete the work in less time.
Key Benefits of Smart Work:
- Requires In-depth Knowledge: Understanding the task thoroughly allows individuals to find effective shortcuts without compromising quality.
- Time-Saving: Smart workers use technology, logic, and creativity to optimize the process, thus saving valuable time.
- Quick Goal Achievement: Instead of rigidly sticking to one method, smart workers adapt their strategies, leading to faster success.
- Strength Building: Smart work encourages personal development by fostering problem-solving skills, resourcefulness, and adaptability.
- Essential for Modern Times: In today’s fast-paced, competitive environment, smart work is vital for staying ahead.
That said, smart work often stems from the foundation laid by hard work. It’s through years of hard work and experience that people learn to work smartly.
Hard Work and Smart Work: Which is Better?
This debate often raises the question—should one prefer hard work or smart work? The reality is that both have their place, and each complements the other. Hard work builds the groundwork, character, and discipline required for success, while smart work refines the process, making it efficient and less time-consuming.
For example, preparing for an important exam may require hard work—studying consistently, memorizing concepts, and practicing regularly. However, applying smart work techniques like making concise notes, using memory tricks, and focusing on high-weightage topics makes the preparation smoother and more effective.
The Ideal Combination: Balance is the Key
Relying solely on one approach may not yield the best results. The perfect formula for success lies in integrating both strategies:
- Work hard initially to understand the basics and build experience.
- Apply smart work to streamline the process, save time, and achieve quicker outcomes.
Think of it as building a house—you need solid groundwork (hard work) and smart architectural planning (smart work) to ensure a strong, beautiful structure.
Real-Life Examples: Smart Work vs Hard Work
- Hard Work Example: A student dedicating 12 hours daily to study every subject in the syllabus without prioritizing.
- Smart Work Example: A student studying strategically by analyzing past papers, focusing on high-scoring topics, and revising efficiently.
Another example can be seen in professional life:
- Hard Work: An employee working overtime manually compiling data reports.
- Smart Work: An employee using software or automation tools to prepare reports quickly and accurately.
Conclusion
Success is not defined solely by how hard you work or how smart you work, but by how well you balance both. The debate of Smart Work vs Hard Work teaches us that while hard work lays the essential groundwork, smart work refines the approach, making the process efficient and goal-oriented.
In the modern era, where time, competition, and innovation play critical roles, integrating both smart and hard work offers the best results. Working hard builds resilience, patience, and discipline, while working smart brings innovation, strategic thinking, and time management.
So, if you’re aiming for success, remember—work hard to build a strong foundation and work smart to reach your goals effectively.
FAQs About Smart Work vs Hard Work
1. What is the key difference between smart work and hard work?
Hard work involves consistent effort and dedication over a long period, while smart work focuses on achieving results efficiently through planning, strategy, and innovation.
2. Is smart work better than hard work?
Both approaches have their benefits. Smart work saves time and enhances productivity, while hard work builds discipline and experience. The best results come from balancing both.
3. Can you succeed with only hard work?
Yes, but it may take longer and be more exhausting. Incorporating smart work strategies can accelerate success.
4. How can one develop smart work skills?
Improving knowledge, learning from experience, using technology, and focusing on effective time management helps in becoming a smart worker.
5. Is smart work a result of hard work?
Yes, often smart work stems from years of hard work, experience, and understanding of how tasks can be optimized.